pan-european assessment, monitoring, and mitigation of stressors on the health of bees
New PoshBee paper tested the effects of glyphosate on bumblebees’ gut microbiome
Pesticides pose a significant threat to pollinators and can have various effects on their health. One way in which pesticides can harm pollinators such as bumblebees is by affecting their gut microbiome, which in turn impacts their immune system and ability to resist parasites.
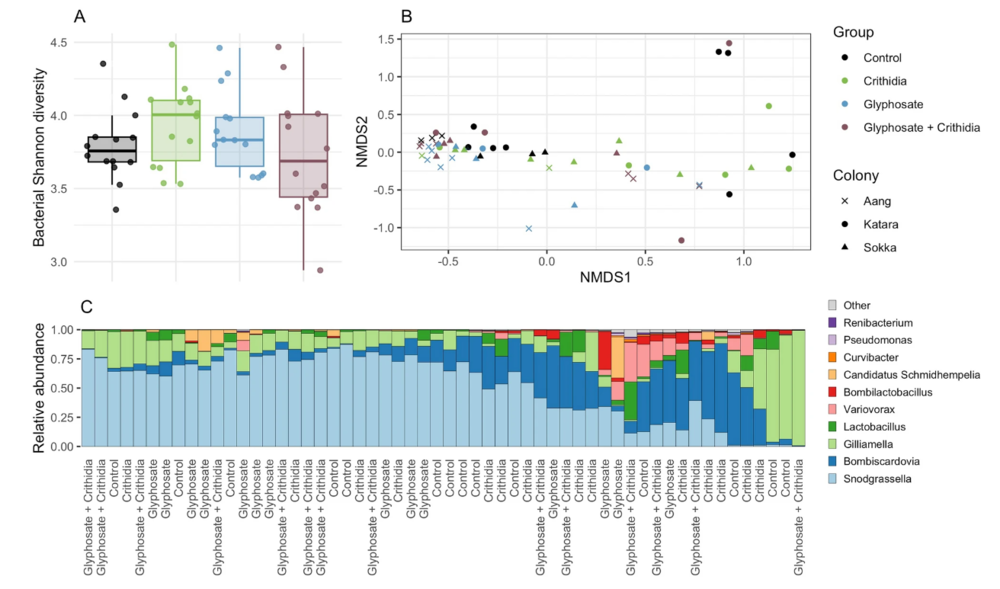
Glyphosate, Crithidia bombi, or their combination have limited effects on bacterial composition of the bumblebee microbiome. (A) Bacterial diversity was evaluated by 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing. (B) Clustering of non-metric multi-dimensional scaling (NMDS) plots of Bray–Curtis dissimilarities. (C) Gut microbiome composition at the genus level.
A new PoshBee study examined the effects of high acute oral dose of glyphosate, a commonly used pesticide, on the gut microbiome of the buff-tailed bumblebee (Bombus terrestris). Glyphosate’s interaction with the gut parasite Crithidia bombi was also examined.
No impacts on the bumblebees’ gut microbiome were observed of glyphosate, C. bombi, or their combination. This finding emphasises the need for caution when extrapolating gut microbiome findings from Apis mellifera to other bee species since studies conducted on honeybees found that glyphosate consistently affected the composition of gut bacteria.
Read the full paper here.